@Controller:修饰class,用来创建处理http请求的对象@RestController:Spring4之后加入的注解,原来在@Controller中返回json需要@ResponseBody来配合,如果直接用@RestController替代@Controller就不需要再配置@ResponseBody,默认返回json格式。@RequestMapping:配置url映射
下面我们尝试使用Spring MVC来实现一组对User对象操作的RESTful API,配合注释详细说明在Spring MVC中如何映射HTTP请求、如何传参、如何编写单元测试。
RESTful API具体设计如下:
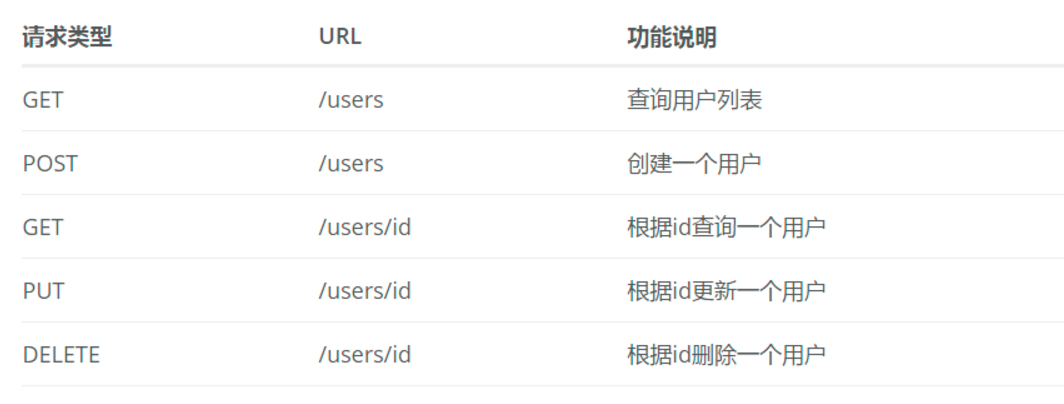
User实体定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
|
实现对User对象的操作接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
private static Map<Long, User> users = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Long, User>());
@GetMapping("/")
public List<User> getUserList() {
return new ArrayList<User>(users.values());
}
@PostMapping("/")
public String postUser(@RequestBody User user) {
users.put(user.getId(), user);
return "success";
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return users.get(id);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public String putUser(@PathVariable Long id, @ModelAttribute User user) {
User u = users.get(id);
u.setName(user.getName());
u.setAge(user.getAge());
users.put(id, u);
return "success";
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
users.remove(id);
return "success";
}
}
|
下面针对该Controller编写测试用例验证正确性,具体如下。当然也可以通过浏览器插件等进行请求提交验证。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(classes = MockServletContext.class)
@WebAppConfiguration
public class ApplicationTests {
private MockMvc mvc;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
mvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new UserController()).build();
}
@Test
public void testUserController() throws Exception {
RequestBuilder request = null;
request = get("/users/");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("[]")));
request = post("/users/")
.param("id", "1")
.param("name", "测试大师")
.param("age", "20");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("success")));
request = get("/users/");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("[{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"测试大师\",\"age\":20}]")));
request = put("/users/1")
.param("name", "测试终极大师")
.param("age", "30");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("success")));
request = get("/users/1");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"测试终极大师\",\"age\":30}")));
request = delete("/users/1");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("success")));
request = get("/users/");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("[]")));
}
}
|
至此,我们通过引入web模块(没有做其他的任何配置),就可以轻松利用Spring MVC的功能,以非常简洁的代码完成了对User对象的RESTful API的创建以及单元测试的编写。其中同时介绍了Spring MVC中最为常用的几个核心注解:@Controller,@RestController,RequestMapping以及一些参数绑定的注解:@PathVariable,@ModelAttribute,@RequestParam等。
文章转自 “程序猿DD” 博客 .



